Antique Arms & Militaria
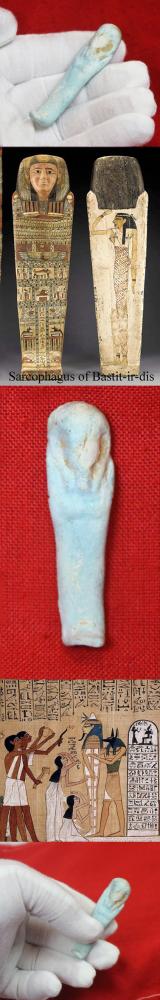
An Original Ancient Egyptian Shabti, The Afterlife Servant of The Mummy, Partial Blue-Glazed Faience 664 to 332 BC
A stunning Grand Tour artefact.
Much of our Grand Tour historic artefacts were originally acquired by a noble Scottish family in the 1820's while on a Grand Tour of the Middle East and the Holy Land, plus Anglo French battle sites within Northern & Western France from Azincourt, in the Pas-de-Calais, to Poitiers in Aquitaine. And the great classical battle sites of Ancient Rome and Greece.
The Scottish 10th Duke of Hamilton, the world renown Grand Tour collector, especially of ancient Egyptian pieces. He was the Ambassador to Catherine the Great as well as being Lord High Steward to both King William IV and Queen Victoria. He was so enamoured with his devotion to his collection of antiquities, he was mummified after his death, and buried in an ancient Egyptian sarcophagus within his family tomb.
From the 25th dynasty to the Late Period. One of a group of fine small tomb pieces we acquired. A shabti (also known as shawabti or ushabti) is a generally mummiform small figurine found in many ancient Egyptian tombs. They are commonly made of blue or green glazed Egyptian faience, but can also consist of stone, wood, clay, metal, and glass. The meaning of the Egyptian term is still debated, however one possible translation is ‘answerer’, as they were believed to answer their master’s call to work in the afterlife. Since the Fourth Dynasty (2613–2494 BC), for instance, the deceased were buried with servant statuettes like bakers and butchers, providing their owners with eternal sustenance. after the death of Cleopatra in around 37 b.c. and the close of the Ptolomeic Dynasty, no shabti were produced for service in Egyptian mummy's tombs. A spell was oft written on the shabti so that it would awaken as planned, this is the 'shabti spell' from chapter six of the Book of the Dead and reads as follows:
"O shawabti, if name of deceased is called upon,
If he is appointed to do any work which is done on the necropolis,
Even as the man is bounden, namely to cultivate the fields,
To flood the river-banks or to carry the sand of the East to the West,
And back again, then 'Here am I!' you shall say"
Piye established the Twenty-fifth Dynasty and appointed the defeated rulers as his provincial governors. He was succeeded first by his brother, Shabaka, and then by his two sons Shebitku and Taharqa. The reunited Nile valley empire of the 25th Dynasty was as large as it had been since the New Kingdom. Pharaohs of the dynasty, among them Taharqa, built or restored temples and monuments throughout the Nile valley, including at Memphis, Karnak, Kawa, and Jebel Barkal. The 25th Dynasty ended with its rulers retreating to their spiritual homeland at Napata. It was there (at El-Kurru and Nuri) that all 25th Dynasty pharaohs were buried under the first pyramids to be constructed in the Nile valley in hundreds of years
The Late Dynasty Period era;
The Twenty-Eighth Dynasty consisted of a single king, Amyrtaeus, prince of Sais, who successfully rebelled against the Persians, inaugurating Egypt's last significant phase of independence under native sovereigns. He left no monuments with his name. This dynasty reigned for six years, from 404 BC–398 BC.
The Twenty-Ninth Dynasty ruled from Mendes, for the period from 398 to 380 BC. King Hakor of this dynasty was able to defeat a Persian invasion during his reign.
The Thirtieth Dynasty took their art style from the Twenty-Sixth Dynasty. A series of three pharaohs ruled from 380 to 343 BC. The first king of the dynasty, Nectanebo I, defeated a Persian invasion in 373 BC. His successor Teos subsequently led an expedition against the Achaemenid Empire in the Near East. The expedition was beginning to meet with some success. unfortunately for Teos, his brother Tjahapimu was plotting against him. Tjahapimu convinced his son Nectanebo II to rebel against Teos and to make himself pharaoh. The plan was successful and the betrayed Teos had no alternative but to flee and the expedition disintegrated. The final ruler of this dynasty, and the final native ruler of Egypt, was Nectanebo II who was defeated in battle leading to the re-annexation by the Achaemenid Empire.
31st Dynasty
Main article: Thirty-first Dynasty of Egypt
The Second Achaemenid Period saw the re-inclusion of Egypt as a satrapy of the Persian Empire under the rule of the Thirty-First Dynasty, (343–332 BC) which consisted of three Persian emperors who ruled as Pharaoh - Artaxerxes III (343–338 BC), Artaxerxes IV (338–336 BC), and Darius III (336–332 BC) - interrupted by the revolt of the non-Achaemenid Khababash (338–335 BC). Persian rule in Egypt ended with the defeat of the Achaemenid Empire by Alexander the Great, who accepted the surrender of the Persian satrap of Egypt Mazaces in 332BC, and marking the beginning of Hellenistic rule in Egypt, which stabilized after Alexander's death into the Ptolemaic Kingdom.
2.5 inches long read more
285.00 GBP
Archaic Zhou Dynasty Bronze Halberd or ‘Ge’ of a Zhou Dynasty Charioteer, Circa 5th Century BC. Used By a Warrior In the Period of the Great Military Doctrine 'The Art of War' by General Sun-Tzu
This is the very type of original ancient ceremonial halbard, defined by the ancient Chinese as a dagger axe 'Ge' and exactly the type as used by the warriors serving under the world renowned General Sun Tzu, in the Kingdom of Wu, who is thought by many to be the finest general, philosopher and military tactician who ever lived. His 2500 year old book on the methods of warfare, tactics and psychology are still taught and highly revered in practically every officer training college throughout the world.
In excavated condition, cast in one piece, slightly curved terminal blade of thin flattened-diamond section, pierced along a basal flange with three slots, with fabulous areas of crystallized malachite, blue/green patina.
We also show in the gallery a schematic of how this 'Ge' halbard would have been mounted 2500 odd years ago on its long haft, and used by a charioteer warrior, there is also one depicted being carried in a painting that we show in the gallery being used in a chariot charge in the Zhou dynasty.
This is a superb original ancient piece from one of the great eras of Chinese history. it is unsigned but near identical to another that was signed and inscribed with details that have now been fully translated, deciphered and a few years ago shown at Sothebys New York estimated to a sale value of $300,000. Its research details are fully listed below, and it is photographed within our gallery for the viewers comparison. Naturally, our un-inscribed, but still, very rare original version, from the same era and place, is a much more affordable fraction of this price
The signed and named Sotheby's of New York example that we show in the gallery, was formerly made for its original warrior owner, Qu Shutuo of Chu, it is from the same period and in similar condition as ours. We reference it's description below, and it is photographed within the gallery, it is finely cast with the elongated yuan divided by a raised ridge in the middle of each side and extending downward to form the hu, inscribed to one side with eight characters reading Chu Qu Shutuo, Qu X zhisun, all bordered by sharply finished edges, the end pierced with three vertically arranged chuan (apertures), the nei with a further rectangular chuan and decorated with hook motifs, inscribed to one side with seven characters reading Chuwang zhi yuanyou, wang zhong, and the other side with five characters reading yu fou zhi X sheng, the surface patinated to a dark silver tone with light malachite encrustation
An Exhibition of Ancient Chinese Ritual Bronzes. Loaned by C.T. Loo & Co., The Detroit Institute of Arts, Detroit, 1940, pl. XXXIII.
New Orleans Museum of Art, New Orleans, March - June 1948.
This inscribed bronze halberd blade, although typical in form, is uniquely important as its inscription serves as a critical primary source that reveals the name of its original owner: Qu Shutuo of Chu. The only known close counterpart to this blade is a damaged bronze halberd blade, missing the yuan, and inscribed on the hu with seven characters, which can be generally translated to ‘for the auspicious use of Qu Shutuo of Chu’. That halberd is now in the collection of the Hunan Provincial Museum, Hunan, and published in Wu Zhenfeng, Shangzhou qingtongqi mingwen ji tuxiang jicheng Compendium of inscriptions and images of bronzes from Shang and Zhou dynasties, vol. 32, Shanghai, 2012, no. 17048
The remaining thirteen inscriptions can be translated as: 'Qu Shutuo of Chu, Qu X's grandson, yuanyou of the King of Chu'. Based on the inscription, the owner of this blade can be identified as such.
See for reference; The Junkunc Collection: Arts of Ancient China / Sotheby's New York
Lot 111
We also show in the gallery a photo of another similar halberd from a museum exhibition, of a Chinese ancient king bodyguard’s halberd gilt pole mounts for his personal charioteer
This is one of a stunning collection of original archaic bronze age weaponry we have just acquired. Many are near identical to other similar examples held in the Metropolitan in New York, the British royal collection, and such as the Hunan Provincial Museum, Hunan, China. As with all our items, every piece is accompanied by a certificate of authenticity. read more
1850.00 GBP
An Original, Roman Republic & Empire Period Bronze Dagger Pommel Ist Cent BC
A super, small collection of original, historical, Imperial Roman and Crusader's artefacts has just been acquired by us and will be added over the next week or so.
Made for, and used by, either a Roman noble, senator or gladiator. It may well even be the same form of dagger a pugio that was used to assassinate Julius Caesar on the Ides of March. The blade grip and scabbard have not survived as is more than usual. A superb Roman dagger mount from the historical time of Julius Caesar, the first Emperor, Augustus, Mark Anthony and Cleopatra, and last, but not least, Jesus of Nazareth. The Ides of March comes from the ides, a term the Romans used to note the middle of a month. Every month has an ides around the middle (as well as a calends at the beginning of the month and nones eight days before the ides). The Ides of March feels special for a couple of reasons: it's the day Caesar was murdered, and it's the subject of a soothsayer's spooky prophecy in William Shakespeare's Julius Caesar. Before Caesar, Roman nobility and military were free to plunder the provinces they ruled. But under Caesar, Rome controlled the process and sent inspectors to check up on everything, so they could only exploit their provinces under Caesar's supervision.
That slight was compounded by Caesar's rebranding of political real estate in his name ? he built statues in his image and renamed monuments for himself. He brought power to his family by giving them political appointments and honorifics, and drew allies outside the charmed circle of Roman nobility, like his soldiers and leaders in the provinces. As far as epic betrayals go, we tend to imagine Brutus in the same league as Judas. In reality, that infamy should be reserved for someone called Decimus.
Caesar trusted Decimus much more than he trusted Brutus ? and that made his betrayal more shocking. Misspelled in Shakespeare's Julius Caesar as "Decius," Decimus was much more important than most of us realize. "There were three leaders of the assassins' conspiracy, Brutus, Cassius, and Decimus." Decimus dined with Caesar the night before his assassination and convinced Caesar to leave his house the next morning (he was staying home because his wife, Calpurnia, was worried). Decimus' betrayal followed an adult life spent at Caesar's side. Brutus, however, had often fought against Caesar, like when he took Pompey's side against Caesar in the Civil War that lasted from 49 to 45 BC. He only came over to Caesar's side after a handsome cash award and profitable political appointment. When he was stabbed, most of the sources say he tried to get up and escape. Unfortunately for Caesar, the conspirators were trained soldiers, so they'd formed a tight perimeter. "They knew how you carry out an ambush,and some of the senators were assigned the job of crowd control."
As far as what Caesar said when he died, "Et tu, Brute" is a Renaissance invention. But Caesar did perform a few resonant gestures. He tried to escape, like any soldier would, but when death was near, he covered his face before he died. It may have been an attempt to preserve his dignity. Bibilography; Professor Strauss, Cornell, Classics and History. As with all our items it comes complete with our certificate of authenticity. read more
145.00 GBP
Good Heavy Original Italian Infantry Papal Army Helmet Cabasset c.1570 From The Papal Armoury
Good Heavy Italian Infantry Helmet Cabasset c.1570, hammered steel raised from a single plate, medial ridge with pear stalk finial, border retains its original brass rosettes (2 missing) each embossed with a ring of 6 stars, stepped flared brim with turned over edge, retaining original linen lining band inside. 19cms tall. Good condition. Provenance: The
Papal Armoury; and London dealers Fenton & Sons Ltd. Fenton and Sons, Antique Arms and Armour, traded in London from 1894-1927. and supplied, amongst others, the British Museum. [Interesting aside, we used to supply them, [Fentons] in the 1920's]. This and a few others were acquired by Fentons in 1919 and were listed in their catalogue. They were all from the Papal Armoury in Rome made for the Barberini family.
The Barberinis supplied the armour and cabassets for the papal army in the late 16th century, a period fraught with anarchy and bandits and direct attacks on papal territories by Parma. The close association led to Maffeo Barberini becoming Pope Urban VIII. His brother Taddeo was made Supreme Commander of the Papal Army. The helmets, including this one, were from the papal armoury and served through the papal wars. It is estimated that about 4500 men served the papal army and most would have worn cabassets, making the original number of the group well over 4000. Others from the group are now in the Musio Storico Vaticano the Old Papal armoury now in the Vatican Historical Museum in the Lateran Palace, Rome. The Papal Army was the loosely-construed army of volunteers and mercenaries in the service of the Italian Papal States, active from the 8th century until the capture of Rome by Italy in 1870. The Papal States maintained a sizeable military during the Middle Ages, using it to fight against the Holy Roman Empire and its Ghibelline allies. During the 1300s, the Papal States began to employ the services of condottieri, mercenaries who sold their services to the extremely wealthy Catholic Church. These forces would be instrumental to the defence of the Pope during the Italian Wars of the 15th and 16th centuries, with Cesare Borgia leading the Papal Army on a campaign of conquest that added several new city-states and regions to the Papal States' territories. Painting in the gallery of the Massacre of San Bartolome in the Catholic-Protestant Religious Wars, where the French crown aided by Queen Catherine de Medici, mother of the French King, with the Pope's blessing, slaughtered ten of thousands of Huguenots what is considered the second deadliest religious war in European history (surpassed only by the Thirty Years' War, which took eight million European lives) The pope was so delighted with the massacre he ordered a Te Deum to be sung as a special thanksgiving (a practice continued for many years after) and had a medal struck with the motto Ugonottorum strages, (Latin: " slaughter of the Huguenots 1572" read more
1995.00 GBP
A Superb and Exemplary Original Service Issue Victorian Helmet of the 3rd {Prince of Wales} Regiment of Dragoon Guards
A Beautiful helmet of brass and white metal, with garter badge of the 3DG, overall in superb condition with chinscales. One of the best surviving examples one can see in our out of a museum
The 3rd (Prince of Wales's) Dragoon Guards was a cavalry regiment in the British Army, first raised in 1685 as the Earl of Plymouth's Regiment of Horse. It was renamed as the 3rd Regiment of Dragoon Guards in 1751 and the 3rd (Prince of Wales's) Dragoon Guards in 1765.
From 1809 to the end of the Napoleonic Wars (1803-15), it was in the Peninsula, serving at Talavera (1809), Busaco (1810), Torres Vedras (1810), Albuera (1811), Badajoz (1811), Ciudad Rodrigo (1812), Salamanca (1812), Burgos (1812) and Vitoria (1813).
The regiment then spent most of the 19th century on home service. It charged rioters in Bristol in 1831 and was kept in Ireland on garrison duties during the Crimean War (1854-56).
However, it did deploy to India from 1857 to 1868, and from 1884 to 1895. In 1868, it was also the only British cavalry unit to participate in the Abysinnia Expedition (1867-68).
The regiment was deployed to the Boer War (1899-1902) from 1901 to 1902, taking part in the anti-guerrilla operations in the Transvaal and Orange Free State. It then spent time in Ireland, England and Egypt on garrison duties.
The 3rd Dragoon Guards arrived on the Western Front in October 1914. It remained there for the entire First World War (1914-18), taking part in many engagements including the first and second battles of Ypres (1914 and 1915), Loos (1915), Arras (1917), Cambrai (1917), St Quentin (1918) and Amiens (1918).
British Dragoon Guards Regiments
1st King's Dragoon Guards (1746, from The King's Own Regiment of Horse); amalgamated to form 1st The Queen's Dragoon Guards (1959)
2nd Queen's Dragoon Guards (1746, from The Princess of Wales's Own Regiment of Horse); redesignated 2nd Dragoon Guards (Queen's Bays) (1872); redesignated The Queen's Bays (2nd Dragoon Guards) (1921); amalgamated to form 1st The Queen's Dragoon Guards (1959)
3rd Dragoon Guards (1747, from 4th Regiment of Horse); redesignated 3rd (Prince of Wales's) Dragoon Guards (1765); amalgamated to form 3rd/6th Dragoon Guards (1922); redesignated 3rd Carabiniers (Prince of Wales's Dragoon Guards) (1928); amalgamated with Royal Scots Greys (2nd Dragoons) to form Royal Scots Dragoon Guards (Carabiniers and Greys) (1971)
4th (Royal Irish) Dragoon Guards (1788, from 1st Irish Horse); redesignated 4th Royal Irish Dragoon Guards (1921); amalgamated to form 4th/7th Dragoon Guards (1922); redesignated 4th/7th Royal Dragoon Guards (1936); amalgamated to form Royal Dragoon Guards (1992)
5th Dragoon Guards (1788, from 2nd Irish Horse); redesignated 5th (Princess Charlotte of Wales's) Dragoon Guards (1804); redesignated 5th Dragoon Guards (Princess Charlotte of Wales's) (1920); amalgamated with The Inniskillings (6th Dragoons) to form 5th/6th Dragoons (1922); redesignated 5th Inniskilling Dragoon Guards (1927); redesignated 5th Royal Inniskilling Dragoon Guards (1935); amalgamated to form Royal Dragoon Guards (1992)
6th Dragoon Guards (The Carabiniers) (1788, from 3rd Irish Horse); redesignated The Carabiniers (6th Dragoon Guards) (1920); amalgamated to form 3rd/6th Dragoon Guards (1922)
7th (The Princess Royal's) Dragoon Guards (1788, from 4th Irish Horse); redesignated 7th Dragoon Guards (Princess Royal's) (1921); amalgamated to form 4th/7th Dragoon Guards (1922)
The Dragoon Guards regiments were converted to armoured cars and tanks during the 1930s. There are still three Dragoon Guards regiments in the British Army:
No liner, the regular plume would be black and red. Army practice it’s likely that different coloured plumes, other than their regular colours, relate to Trumpeters and Farriers (as still practised in the Household Cavalry). A very light and small amount of denting to the skull. read more
1850.00 GBP
A Most Fine Presentation 2nd Manchester, 33rd Lancashire Rifle Volunteers Antique Victorian Sword of 1869
Presented to Captain Henry Lewis Rocca, [Later Colonel of the regiment] by the members of No.10 Company. This sword was likely presented by his volunteer company on his promotion to captain in November 1869. Stunning bright polished steel fittings, revealed after over 12 hours of no expense spared, specialist artisan hand conservation, and an absolutely amazing condition deluxe presentation blade with mirror bright finish.
He was born in Hamburg, Germany in 1831, and came to England in 1851, he settled in Manchester and in 1857 became a naturalised British subject. Later he became the principal of a firm of merchants and shippers. He joined the 2nd Manchester 33rd Lancashire Rifle Volunteers, the Ardwick Corps in the summer of 1866 and, although offered a commission, he insisted on drilling in the ranks until he became proficient.
He was appointed Lt on 19th November 1866. Capt on 3rd November 1869, Maj on 10th January 1877 and Lt-Col 10 Jan. 1885.
He was one of the first recipients of the first
issue of the Volunteer Officers' decoration. he died on the 27 Dec. 1916.
Henry Rocca aged 43 took over command as Colonel of the Ardwick Corps in December 1885, the headquarters were still in the original old house at 1 Ardwick Green. One of his first priorities was the provision of a proper home for the Volunteers. It was decided that the most sensible and practical course was to buy the existing building which had been their HQ for so many years and at the same time acquire the free-hold of the site. Rather than carry out the usual methods of raising funds for such a
project by soliciting donations and holding fund-raising bazaars, Colonel Rocca generously provided the necessary funds at a low rate of interest. This to be repaid out of the Government capitation grants as circumstances permitted, and this arrangement was sanctioned by the War Office, allowing planning to proceed
Manchester and its neighbouring townships were no strangers to the raising of volunteer soldiers and their mustering for war.
Following the capitulation of 'Gentleman Johnny' Burgoyne's army on 17 October 1777 at Saratoga there were many offers of armed and financial assistance from patriotic citizens. Manchester raised the 'Royal Manchester Volunteers' or 72nd Regiment of Foot who serve with distinction in the garrison of Gibraltar throughout the siege 1783. There was much local enthusiasm both to subscribe money and to this Regiment. Within four months the Regiment had been completely officered, equipped and was ready for service. All of this was from local resources. In 1793 the outbreak of yet another war with France produced a wave of s enthusiasm, resulting in the formation of a Manchester Military Association raising of the Royal Manchester Volunteers or 104th Regiment of Foot.
The fear of invasion saw the raising of two battalions of Manchester and Salford volunteers in February 1797. In 1798 Colonel Ackers raised a second Volunteer Regiment.
Enthusiasm continued and in December there was a proposal to raise yet another body of men to be known as The (Town's Own) Loyal Regiment of Infantry read more
1125.00 GBP
A Beautiful Indo Persian 'Tiger's Claw' Khanjar Walrus Sea Ivory and Wootz Watered Steel Bladed Dagger,
A Magnificent 'Tiger's Claw' Wootz steel blade, likely in mottled pattern, with carved walrus sea ivory handle dagger 18th to 19th century. A museum grade quality piece. Once the property of a high status Mughal noble or prince. Elegant double-edged tapering steel blade of curved form with raised central spine. The blade has a very fine wootz watered steel pattern. The fine steel dagger is attached to a thick carved and engraved ivory handle. This waisted walrus ivory hilt is incised in relief to each side with a tiger capturing a deer and typical Mughul flora and fauna. A most similar example is in the Metropolitan Museum. Small losses to ivory at the base of the handle at the quillon. Walrus ivory is characterized in cross section by a central core that has a marbled appearance, surrounded by a smooth creamy white dentine layer see photo 7 circa 200 to 270 years old. read more
1200.00 GBP
A Superb and Huge 19th Century Solid Hallmarked 800 Silver Mounted Gaucho Knife, By FRIED.HERDER ABR.SOHN SOLINGEN
A stunning German export model, which are certainly the most sought after and desirable of all the silver gaucho knives, especially by the best German makers such as Herder, of Solingen, and the very large examples are particularly rare and desirable, just as the very large antique American Bowie knives are rare
The South American Cowboy or Gaucho was the first range cowboy, whose existence is first recorded back in the 1600's, they wandered the Pampas for centuries, working cattle and living off the land and the herd, just as the later North American Cowboy did in the 19th century. Like the North American cowboys gauchos were generally reputed to be strong, honest, silent types, but proud and capable of violence when provoked. The gaucho tendency to violence over petty matters is also recognised as a typical trait.
Gauchos' use of the famous "facón" (knife generally tucked into the rear of the gaucho sash) is legendary, often associated with considerable bloodletting. Historically, the facón was typically the only eating instrument that a gaucho carried. As Charles Darwin said of the distinctive men who wore and used the facón,
"Many quarrels arose, which from the general manner of fighting with the knife often proved fatal."
This is a very fine quality and unusually large example. 17 inches long overall 10 inch blade.
In 2018 a similar sized example {within 1 inch} sold at Centurion Auctions in Tallahassee, Florida USA for $17,000. {£13,993} read more
2250.00 GBP
A Most Attractive Middle Eastern, Antique 19th Century Jambiya.
Carved wooden hit brass embossed and leather scabbard over wood. Double edged steel blade. The blade would polish nicely. The janbiya was given its name because it is worn on the side of a person – the word janbia is derived from the Arabic word "janb" which mean "side". A jambia is constituted of a handle, a blade, and a sheath in which the blade is held. It is made of a certain sort of wood, to hold the blade that is fixed to the waist from underneath with an upward curved sheath. The belt that holds the janbia can be made of tanned leather, or, wound some thick cloth.
The janbiya handle often tells of the social status of the man who wears it.
Other jambiya hilts are made of different types of horn, wood, metal and ivory. Apart from the material used for the hilt, the design and detail is a measure of its value and the status of its owner. there are 53 different types of Jambiya in the Metropolitan museum Collection, some bear a similarity to this example, many with near identical blades. read more
245.00 GBP
A Fine and Long, Saudi Arabian, Silver & Copper Alloy Dharia Jambiya 19th Century
A rare jambiya to find as the smaller Omani and Yemeni types were made in far greater numbers over the past century. A long bladed Dharia jambiya, with shbeyl hilt type, more within the short-sword size, with a flat beyd blade as opposed to the more frequently seen Omani dagger sized pieces. Late 19th century also called in the west a Wahhabi jambiya. With gemstone set scabbard and covered in geometrically patterned silver. A "Wahhabi jambiya" is a occidental collector's term. "Weapons of the Islamic World" by The King Faisal Centre Centre for Research & Islamic Studies categorises these by type, tribal or regional origin, not by religious sect. Obviously jambiyas of this type were carried by Wahhabis and certain of the tribes they are associated with would be predominately Wahhabi. These are from the Asir, Hejaz, Nejd (generally the South, West and Central Saudi Arabia) and were the origins and backbone of the "Ikwhan" which was of course Wahhabi. Dharia is the term used to describe the long dagger which originates from the west of modern day Saudi Arabia, around the Azir/Hijaz area, and down as far as Yemen.
The word Dharia appears to come from the Arabic Dhura'eyah which translates as Arm Long Dagger. These daggers are also called Sabiki, Sabak, Sabik etc depending on the spelling. The term Wahabite is also commonly used to describe these, but any direct connection with the Wahhabi Movement except perhaps the actual geographical area is likely very co-incidental, and perhaps that this style was one used by them.
The jambia was given its name because it is worn on the side of a person – the word jambia is derived from the Arabic word janb (Arabic: جنب, lit. 'side'). A jambia is constituted of a handle, a blade, and a sheath in which the blade is held. It is made of a certain sort of wood, to hold the blade that is fixed to the waist from underneath with an upward curved sheath. The belt that holds the jambia is made of tanned leather, or some thick cloth. There are specialised markets and handicraft markets that decorate it with golden wires.
The jambia handle often tells of the social status of the man who wears it. Jambias can be made with ivory handles or hilts of other rare and exotic materials.
T. E. Lawrence was famous for using a jambiya knife historically.
Overall just over 21.5 inches long. read more
1125.00 GBP