Antique Arms & Militaria
A South American Sorocabana Knife 'Faca De Ponta’ of the South American Cowboys
"Sorocabana knife". It was the knife used by the bandeirantes of Sao Paulo and by the tropeiros who traveled between the south and southeast regions. Made from an imported blade from Gebruder Weyersberg Solingen. Gilt decorated makers panel. Carved ebony hilt In the southern region of Brazil , "tropeiro" was the conductor of mules troops from the city of Viamao, Rio Grande do Sul, to Sorocaba, Sao Paulo. These troops supplied the gold cycle in Minas Gerais in the eighteenth century. This activity was responsible for the founding of countless cities in the states of Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina and Parana. Before the railways, and long before the trucks, merchandise trade was done by drovers in regions where there were no alternatives for sea or river navigation for distribution.
The interior regions, far from the coast, depended for a long time on this mode of transportation by mules . Since the end of the seventeenth century, mining works, for example, required the formation of groups of merchants in the domestic trade. Initially called men of the way, traffickers or passers-by, the tropeiros became fundamental in the trade of slaves , food and tools of the miners.
Far from being specialized merchants, the tropeiros bought and sold of everything a little: slaves, tools, clothes, etc. The existence of Tropeirismo was intimately related to the coming and going of roads and highways, especially the Estrada Real - road through which Minas Gerais gold arrived at the port of Rio de Janeiro and followed to Portugal . read more
285.00 GBP
Antique Mandingo Chieftain's Slave and Gold Trader Sword With Tattoo'd Leather Scabbard
A chieftain's weapon of Mandingo slave and gold traders. The Manding (Mandingo) are West African people. Their traditional sword for the slave traders comprises a sabre like blade, guardless leather grip and scabbard with exquisite leather work. This example is a long sized example, of a high ranking Mandingo, of very nice quality and finely tattooed. 25 inches long curved blade, leather grip and leather scabbard with leaf shaped widening tip, entirely tooled tattooed and decorated. Of special interest is the finely bound and decorated leather work. These weapons are well known for their leather-work and the tattooing applied to the leather of the scabbards. The iron work skills are less well developed. Many blades are taken from European weapons such as sabres and cutlasses.
While the Baule are a distinct tribal group to the west, it is important to observe that Malinke is a variant term applied to the Mandingo (also Manding, Mandin, Mande).
In general, these remain primarily considered Mandingo weapons, and from regions in Mali. These were of course invariably mounted with European sabre blades. Mandingo Tribe (also known as the Mandinka, Mande, or the Malinke Tribes) were the traders of the African West Coast, trading primarily in gold and slaves from other African tribes. The blades comes out a little from the chape. Small areas of leather separation on the scabbard binding. Picture in the gallery of an 1850's engraving of a Mandingo Chief and his sword bearer. read more
395.00 GBP
An Antique 18th Century Indian Armour Piercing Punch Dagger Katar, Combat Damaged, or Adapted For Armour Wear
The Katar is an amazing combat weapon from the Indian sub continent, in combat use by select warriors and nobles for five centuries, it is a scarcely seen piece, yet highly distinctive and iconic. It was designed in several forms, some long and relatively light, others extremely robust and overtly powerful. This is one of the latter types. It’s ‘crow’s beak’ penetrating tip shows and strongest possible ribbed blade design was so efficient that effectively there was likely no body armour that could not be penetrated by such a powerful piece, once in the hands of a Katar wielding expert. It has been forged in great and powerful quality, and is a very high quality example with superior heft.
One of the bracing arms has been lost, very possibly from an opponents sword cut, although we have seen this before and we were informed by an esteemed elderly Indian warfare scholar that it has been known for one arm to ge removed so an an armoured warrior could use a the Katar while wearing the right fore-arm protector combat armour, known as the the bazu band. While wearing the bazu band armour the warriors forearm is much wider than usual and a Katar’s narrow arm extensions would preclude its use in combat while wearing armour.
The katar originated in Tamil Nadu where its Dravidian name was kattari before being altered to katar in the north. The earliest forms occur in the medieval Deccan kingdom of Vijayanagara. Katar dating back to this period often had a leaf- or shell-like knuckle-guard to protect the back of the hand, but this was discarded by the latter half of the 17th century. The Maratha gauntlet sword or pata is thought to have been developed from the katar. As the weapon spread throughout India it became something of a status symbol, much like the Southeast Asian kris or the Japanese katana. Among the Rajputs, Sikhs and Mughals, princes and nobles were often portrayed wearing a katara at their side. This was not only a precaution for self-defense, but it was also meant to show their wealth and position. Upper-class Mughals would even hunt tigers with katar. For a hunter to kill a tiger with such a short-range weapon was considered the surest sign of bravery and martial skill. The heat and moisture of India's climate made steel an unsuitable material for a dagger sheath, so they were covered in fabric such as velvet or silk. Because the katara's blade is in line with the user's arm, the basic attack is a direct thrust identical to a punch, although it could also be used for slashing. This design allows the fighter to put their whole weight into a thrust. Typical targets include the head and upper body, similar to boxing. The sides of the handle could be used for blocking but it otherwise has little defensive capability. As such, the wielder must be agile enough to dodge the opponent's attacks and strike quickly, made possible because of the weapon's light weight and small size compared to a long sword. Indian martial arts in general make extensive use of agility and acrobatic maneuvers. As far back as the 16th century, there was at least one fighting style which focused on fighting with a pair of katara, one in each hand. read more
345.00 GBP
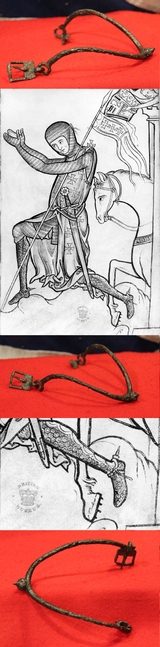
A 1200’s Old Knight's Prick Spur, Still With Buckle From The IInd Baron’s War of Henry IIIrd and Earl Simon de Montfort
We show a medeavil drawing from the British Museum of a kneeling knight wearing the very same form of prick spur. It is absolutely remarkable that this spur stil has its leather strap buckle and mount in place. Battle of Lewes period, from the IInd Baron’s War
The Battle of Lewes was one of two main battles of the conflict known as the Second Barons' War. It took place at Lewes in Sussex, on 14 May 1264.[1] It marked the high point of the career of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, and made him the "uncrowned King of England". Henry III left the safety of Lewes Castle and St. Pancras Priory to engage the barons in battle and was initially successful, his son Prince Edward routing part of the baronial army with a cavalry charge. However, Edward pursued his quarry off the battlefield and left Henry's men exposed. Henry was forced to launch an infantry attack up Offham Hill where he was defeated by the barons' men defending the hilltop. The royalists fled back to the castle and priory and the King was forced to sign the Mise of Lewes, ceding many of his powers to Montfort.
The battle site is still not completely agreed upon, but part of the conflict was recorded at Offham hill, and this is was just 4 miles south of our farm, Thousands of the protagonists soldiers were supposedly camped within our old grounds, but at present it is not certain for which side they fought. Our farm was originally part of Earl Godwin’s estate, later more famously known as King Harold, who also supposedly camped here before his Battle of Hastings in 1066. A Canadian funded documentary is being filmed here at the current time.
Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester (c. 1208 – 4 August 1265), later sometimes referred to as Simon de Montfort to distinguish him from his namesake relatives, was a nobleman of French origin and a member of the English peerage, who led the baronial opposition to the rule of King Henry III of England, culminating in the Second Barons' War. Following his initial victories over royal forces, he became de facto ruler of the country, and played a major role in the constitutional development of England.
During his rule, Montfort called two famous parliaments: the Oxford Parliament stripped Henry of his unlimited authority, while the second included ordinary citizens from the towns. For this reason, Montfort is regarded today as one of the progenitors of modern parliamentary democracy, however during his time as Earl of Leicester he was also determinedly anti semitic and expelled all of the Jews from that city, yet curiously, Leicester's Jews were allowed to move to the eastern suburbs, which were controlled by Montfort's great-aunt Margaret, Countess of Winchester. But as he became ruler of England he also cancelled debts owed to Jews through violent seizures of records. Montfort's party massacred the Jews of London, Worcester and Derby, killing scores of Jews from Winchester to Lincoln. After a rule of just over a year, Montfort was killed by forces loyal to the king in the Battle of Evesham
de Montfort also had connections to the Albigensian Crusade, which was a crusade against the heretic Cathars, and was immensely popular in northern France because it gave pious warriors an opportunity to win a Crusade indulgence. The Albigensian Crusade, Crusade (1209-29) was called by Pope Innocent III against the Cathari, a dualist religious movement in southern France that the Roman Catholic Church had branded heretical. The war pitted the nobility of staunchly Catholic northern France against that of the south, where the Cathari were tolerated and even enjoyed the support of the nobles. Although the Crusade did not eliminate Catharism, it eventually enabled the French king to establish his authority over the south. During the first season the Crusaders captured Boziers in the heart of Cathar territory and following the instructions of the papal legate who allegedly said, Kill them all. God will know his own, when asked how the Crusaders should distinguish the heretics from true Christians massacred almost the entire population of the city. With the exception of Carcassonne, which held out for a few months, much of the territory of the Albigeois surrendered to the Crusaders. Command of the Crusade was then given to Simon, lord of Montfort and earl of Leicester, who had served during the Fourth Crusade. A man, one can safely say was famed for his deeply held religious prejudices, yet ironically, an exponent of parliamentary democracy. read more
475.00 GBP
A Most Scarce Antique Australian Aboriginal Throwing Club, Carved Head
Nulla Nulla, Aboriginal, short, possibly mulga wood, very dense hardwood, throwing club with ovoid shaped head, used for hunting, fighting and ceremonial purposes, [South East] Australia, 1860. A waddy, nulla nulla or hunting stick is an Aboriginal Australian club for use in hunting and fighting. The first of these names comes from the Dharuk Aborigines of Port Jackson, Sydney.
A waddy is a heavy, pointed club constructed of carved timber. Waddies have been used in hand-to-hand combat, and were capable of splitting a shield, and killing or stunning prey. In addition to this they could be employed as a projectile as well as used to make fire and make ochre. They found further use in punishing those who broke Aboriginal law, which often involved settling a conflict between individuals, or between an individual and a group, in a 'Trial by Ordeal' in which fighters gave and suffered heavy blows resulting in skull and bone fractures and much blood read more
375.00 GBP
Antique Zulu-Tsonga Prestige Staff Possibly Carved by a Carver Known as the 'Baboon Master'. With a Carved Female Head
19th century. This dignatory's staff has a most figurative carving. They have been collected in Southern Africa since the mid-19th century. Recent research by Anitra Nettleton suggests, however, that Tsonga sculptors may actually have produced most of these carvings. There is evidence that the Tsonga migrated to the Natal from southern Mozambique as early as the 1850s. Recognized for their carving skills, they were soon producing fine artifacts for Zulu dignatories. Two related staffs, were purchased for the collection of the Standard Bank Foundation in Johannesburg. One staff of theirs is surmounted by a baboon and the other by a male figure with a beard. Both are said to be turn-of-the-century staffs carved by the same hand, by a most accomplished and sought after artist dubbed the 'Baboon Master', who was possibly of Tsonga origin. 31 inches long. read more
750.00 GBP
A Rare 19th Century King's Knife of the Zande or the Mengbetu People, A Trombash Power Authority Knife
A long Knife consisting of a short cylindrical wooden handle, round in section, with a flat end bound in iron banding at the pommel end. The other end of this is cut flat, and has a smaller cylindrical body as the middle hand grip section. Above this point, the handle connects with the blade tang. Which goes through the handle, the tang has been inserted through the centre of the handle, and then its rectangular end hammered over at the top to fix it in place. This is end is visible where it emerges through the handle top, and is off centre. The narrower part of the handle have been decorated with an iron binding strip. Both binding strips [top and bottom] have their ends hammered into slots in the wood to secure them. The blade is curved, with a broad flat ridge running along the length on both sides. This is not centred. On one side of the ridge, the blade extends to form a broad, sharpened base edge with a pointed corner; a more narrow blade extends from the other side of this, slightly higher up the knife. The sides then begin to taper in towards the point at the other end. Both edges were once sharpened. The object is complete, with some minor cut marks on the blade and handle.
Very similar to a Mengbetu collected by Robert Grenville Gayer-Anderson in the Bahr el Ghazal region, probably between 1909 and 1914, in the period immediately before World War I. At the time this object was collected, the Bahr el Ghazal province was much larger than it is today, extending from roughly the Bahr el Arab all the way to the border with the Belgian Congo; this area is now divided into the districts of Western Bahr el Ghazal, Northern Bahr el Ghazal, and parts of Warab, El Buheyrat and Western Equatoria. The drawing in the gallery is a 19th century depiction of Munza, the king of the Mangbetu. Seated on his throne, he holds a similar knife to ours as a symbol of power and authority. read more
395.00 GBP
A Beautiful Sword of the Mandinka, West African, with Elaborate Decorative Fittings 20th. Century
Curved on both sides, fluted back blade with baluster contrast stitching and leather-covered handle. Geometrically patterned leather scabbard with traditional banding patterns, stitched raffia decorations and braided suspension cords and leather fringe tassels.
In some areas they are referred to locally as termed a 'kota' and that the scabbard was termed 'holga' ( house 'for the sword')
The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia and the Casamance region in Senegal to Ivory Coast. Although widespread, the Mandinka constitute the largest ethnic group only in the countries of Mali, Guinea and The Gambia. Most Mandinka live in family-related compounds in traditional rural villages. Their traditional society has featured socially stratified castes.Mandinka communities have been fairly autonomous and self-ruled, being led by a chief and group of elders. Mandinka has been an oral society, where mythologies, history and knowledge are verbally transmitted from one generation to the next. Their music and literary traditions are preserved by a caste of griots, known locally as jelis, as well as guilds and brotherhoods like the donso (hunters).
Between the 16th and 19th centuries, many Muslim and non-Muslim Mandinka people, along with numerous other African ethnic groups, were captured, enslaved and shipped to the Americas. They intermixed with slaves and workers of other ethnicities, creating a Creole culture. The Mandinka people significantly influenced the African heritage of descended peoples now found in Brazil, the Southern United States and, to a lesser extent, the Caribbean read more
195.00 GBP
A Most Charming Napoleonic Wars King George IIIrd Royal Scot's Greys Officer's Carved Horn, Campaign Drinking Cup
In carved horn used from the 1790's by a British Napoleonic Wars officer in the Royal Scot's Greys, then by his grandson in the Crimean war. A super Napoleonic Wars collectable.
Campaign furniture is an umbrella term for the portable items of furniture used by the military in the eighteenth, nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. It is comprised of a huge number of objects, from leatherwork, knives and forks, flasks, drinking vessels, chairs to chests, wardrobes to washstands and games tables to camp beds. from chairs to chests, wardrobes to washstands and games tables to camp beds. A number of celebrated British furniture makers created pieces of campaign furniture, elevating it beyond its roots in functional, army-based design to desirable, collectable decor that continues to add a beautiful, innovative touch to homes today. read more
145.00 GBP
A Most Scarce and Beautiful African Congo Tribal Warrior's Shield, of the Mongo Tribe.
Long ovoid form shield with stunning geometric pattern decoration. Carved wood with rattan bound edging.
The Mongo are one of the Bantu groups of Central Africa, forming the second largest ethnic group in the Democratic Republic of Congo. They are a diverse collection of peoples living in the equatorial forest, south of the main Congo River bend and north of the Kasai and Sankuru Rivers. This area is in the south of the province of Equateur and the north of Bandundu Province.
The Mongo speak either the Mongo language (also called Nkundo) or one of the related languages in the Bantu Mongo family. The Lingala language, however, often replaces Mongo in urban centers. Along with the Luba and the Kongo, they are the three largest ethnic groups in the country.
The Mongo ethnic group is divided into several tribes including Bolia, Bokote, Bongandu, Iyaelima, Konda, Mbole, Nkutu, Ntomba, Sengele, Songomeno, Dengese and Tetela-Kusu, Bakutu, Boyela.
Antique & Vintage original African tribal art is now some of the most desirable and sophisticated decor for national and international interior decorators.
Fine tribal artefacts have always been highly popular and in regards to interior decor, the height of sophistication, but recently it has become absolutely 'the' collectable art of the moment. As to be seen from far afield interiors such as in the 8th Arrondissement, in Paris particularly Avenue Montaigne, to Park Avenue New York, to Kensington Palace Gardens in London or the Piazza di Spagna, Via Condotti and Via del Babuino in Rome. All of the above we have had clients for such African tribal art and weaponry, as a statement focal point for their interior decor.
Super colour contrasts and design incorporating red ochre, cobalt blue, black and white. Red ochre is one of the very earliest pigments used by man, dating back to prehistoric times where it’s use is the basis of many Stone Age cave paintings
Overall in very good condition for age.
16 inches x 35 inches read more
875.00 GBP